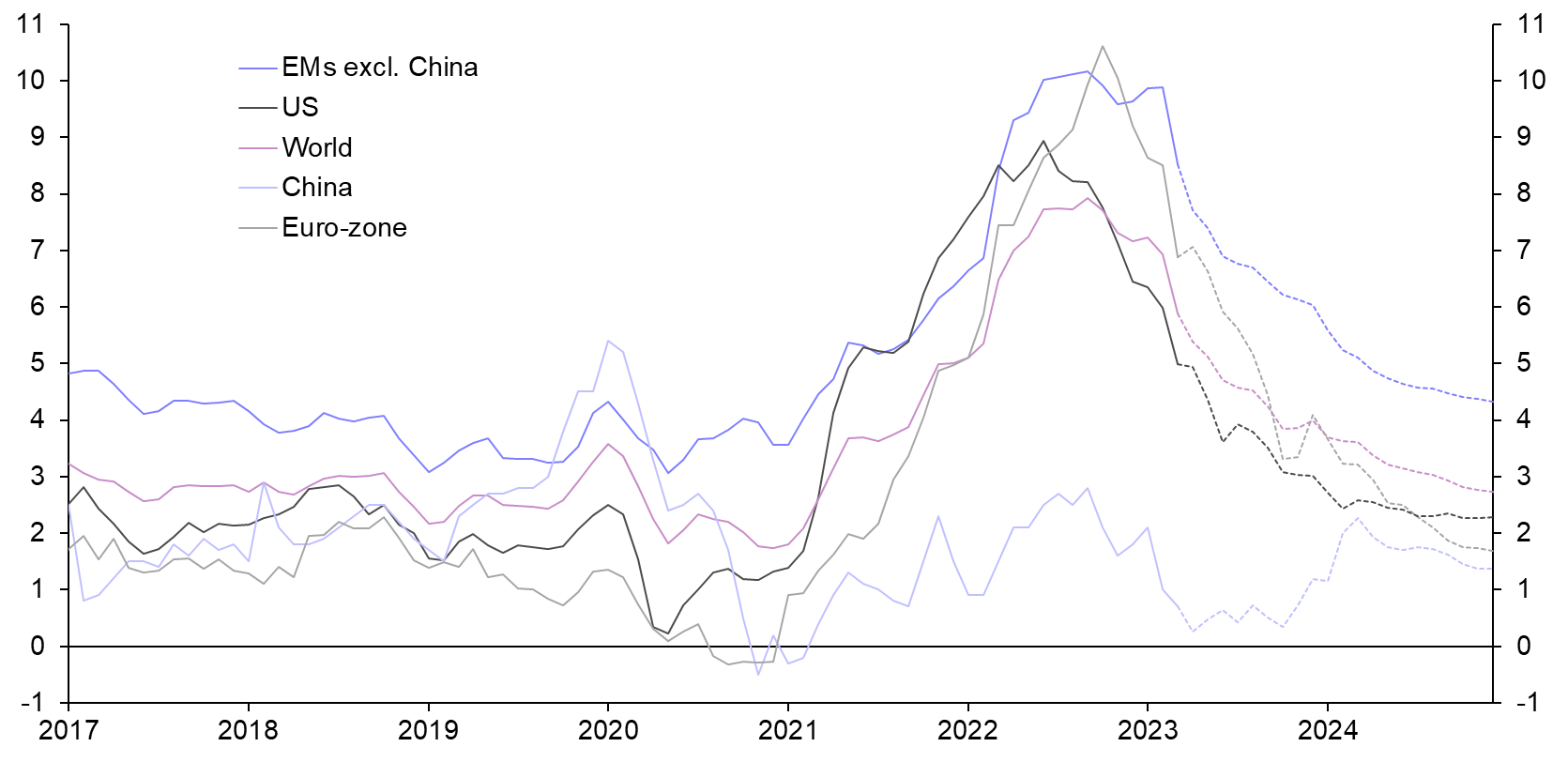
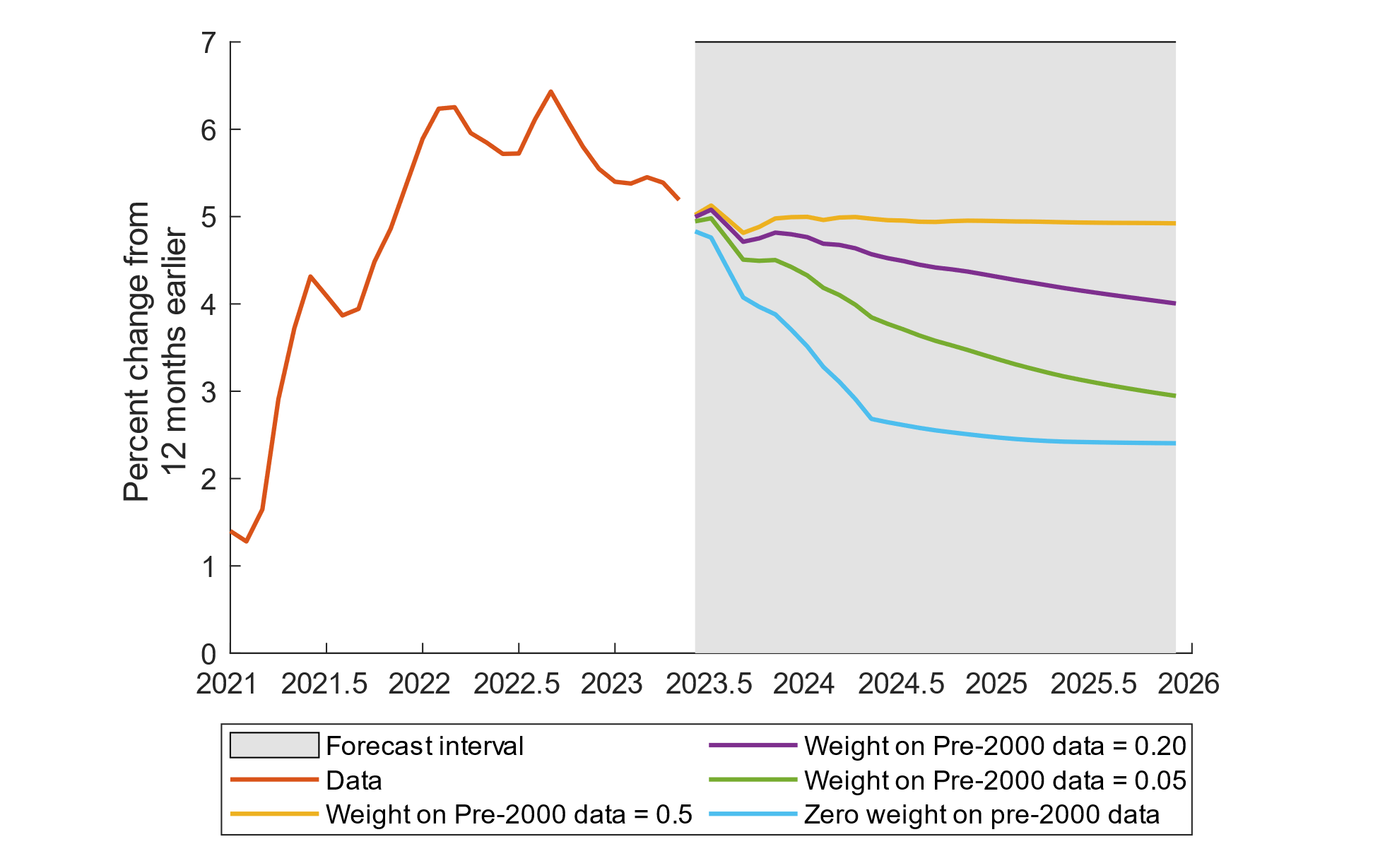
As the world moves toward 2025, inflation continues to be a critical factor shaping global economies. Whether you're an investor, a business owner, or simply someone managing personal finances, understanding inflation trends is essential. Inflation 2025 will likely bring about significant changes, impacting everything from consumer purchasing power to investment strategies. This article will delve deep into what inflation means for the future, exploring its causes, effects, and potential solutions.
Throughout history, inflation has been a double-edged sword. While moderate inflation can signify a healthy, growing economy, excessive inflation can lead to financial instability. As we approach 2025, experts predict that inflation could become a dominant force in shaping economic policies worldwide. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of inflation trends, helping you navigate the challenges and seize the opportunities ahead.
By the end of this article, you'll gain a clearer understanding of inflation's impact on global markets, consumer behavior, and investment strategies. Whether you're looking to protect your assets or explore new opportunities, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to thrive in the evolving economic landscape of 2025.
Read also:Unlock The Secrets Of 7to A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- What is Inflation?
- Causes of Inflation
- Effects of Inflation on the Economy
- Global Inflation Trends
- Inflation Forecast for 2025
- Impact of Inflation on Consumers
- Investment Strategies Amid Rising Inflation
- Government Policies to Combat Inflation
- Historical Perspective on Inflation
- Conclusion
What is Inflation?
Inflation refers to the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time. When inflation occurs, the purchasing power of money decreases, meaning that each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Inflation is typically measured using indices such as the Consumer Price Index (CPI) or Producer Price Index (PPI).
Understanding inflation is crucial because it affects everything from everyday expenses to long-term financial planning. Moderate inflation is generally considered a sign of a growing economy, but excessive inflation can lead to economic instability, eroding savings and reducing consumer confidence.
Types of Inflation
- Creeping Inflation: A slow and steady increase in prices, typically below 3% annually.
- Walking Inflation: A faster rate of inflation, usually between 3% and 10% annually.
- Galloping Inflation: Extremely high inflation rates, often above 10%, which can severely disrupt economies.
- Hyperinflation: An out-of-control inflation rate, often exceeding 50% per month, which can collapse entire economies.
Causes of Inflation
Inflation can arise from various factors, including demand-pull, cost-push, and built-in inflation. Each type has distinct characteristics and impacts on the economy.
Demand-Pull Inflation
Demand-pull inflation occurs when the demand for goods and services exceeds supply. This can happen during periods of economic growth when consumers have more disposable income and businesses struggle to meet rising demand.
Cost-Push Inflation
Cost-push inflation happens when the costs of production increase, leading to higher prices for consumers. Factors such as rising wages, increased raw material costs, or supply chain disruptions can contribute to cost-push inflation.
Built-In Inflation
Built-in inflation, also known as wage-price spiral, occurs when workers demand higher wages to keep up with rising living costs. This can lead to a cycle of increasing prices and wages, perpetuating inflation.
Read also:Extreme Body Modification A Comprehensive Guide To Bme Practices
Effects of Inflation on the Economy
Inflation has far-reaching effects on economies, influencing everything from consumer behavior to government policies. While moderate inflation can stimulate economic growth, excessive inflation can lead to severe consequences.
Positive Effects
- Encourages Spending: When people anticipate rising prices, they may spend more now rather than later, boosting economic activity.
- Reduces Debt Burden: Inflation erodes the real value of debt, making it easier for borrowers to repay loans.
Negative Effects
- Reduces Purchasing Power: As prices rise, consumers can afford fewer goods and services with the same amount of money.
- Uncertainty and Instability: High inflation can create uncertainty, discouraging investment and saving.
Global Inflation Trends
Global inflation trends vary significantly across regions, influenced by factors such as monetary policies, geopolitical events, and technological advancements. In recent years, inflation has been on the rise in many parts of the world, driven by supply chain disruptions and increasing energy costs.
According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), global inflation is expected to remain elevated through 2025, with developing economies experiencing higher rates compared to advanced economies. This trend underscores the importance of proactive measures to mitigate inflation's impact.
Inflation Forecast for 2025
Looking ahead to 2025, economists predict that inflation will continue to be a significant concern. Key factors contributing to this forecast include:
- Central Bank Policies: Many central banks are expected to maintain accommodative monetary policies to support economic recovery, potentially fueling inflation.
- Supply Chain Challenges: Persistent supply chain disruptions could lead to higher production costs, driving up prices.
- Energy Prices: Fluctuations in global energy markets could significantly impact inflation rates, particularly in energy-dependent economies.
While inflation forecasts vary, most experts agree that proactive measures are essential to manage its effects on economies and individuals.
Impact of Inflation on Consumers
Inflation directly affects consumers by reducing their purchasing power and altering spending habits. As prices rise, consumers may need to allocate more of their income toward essential goods and services, leaving less for discretionary spending.
To cope with inflation, consumers can adopt strategies such as budgeting, saving, and investing in assets that provide inflation protection. Additionally, staying informed about economic trends and government policies can help consumers make better financial decisions.
Investment Strategies Amid Rising Inflation
Investors can protect their portfolios from inflation by diversifying their assets and focusing on investments that historically perform well during inflationary periods. Some effective strategies include:
- Real Assets: Investing in real estate, commodities, and precious metals can provide a hedge against inflation.
- Stocks: Companies with strong pricing power and robust business models tend to outperform during inflationary times.
- Inflation-Linked Bonds: These bonds adjust their principal value based on inflation, offering protection against rising prices.
Consulting with a financial advisor can also help investors tailor their strategies to their specific goals and risk tolerance.
Government Policies to Combat Inflation
Governments and central banks employ various tools to manage inflation, including monetary and fiscal policies. Key measures include:
- Interest Rate Adjustments: Central banks can raise interest rates to reduce borrowing and spending, thereby curbing inflation.
- Fiscal Policies: Governments can implement tax reforms and spending cuts to control inflationary pressures.
- Monetary Policies: Central banks can adjust money supply through quantitative tightening or other measures to stabilize inflation.
Effective policy implementation requires careful monitoring of economic indicators and collaboration between governments and central banks.
Historical Perspective on Inflation
Throughout history, inflation has played a pivotal role in shaping economies. From the hyperinflation of the Weimar Republic in the early 20th century to the stagflation of the 1970s, lessons learned from past experiences can inform future policies.
By studying historical inflation trends, policymakers and economists can better anticipate challenges and develop strategies to mitigate inflation's impact. This historical context is crucial for understanding the complexities of inflation and its implications for the future.
Conclusion
Inflation 2025 presents both challenges and opportunities for economies and individuals worldwide. By understanding its causes, effects, and potential solutions, you can better navigate the evolving economic landscape. Whether through prudent financial planning, strategic investments, or informed policy decisions, managing inflation is essential for long-term success.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and insights in the comments below. Additionally, explore other articles on our site to deepen your understanding of economic trends and personal finance strategies. Together, we can build a more resilient and prosperous future.
Data sources: International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Bank, Federal Reserve, and reputable economic research institutions.