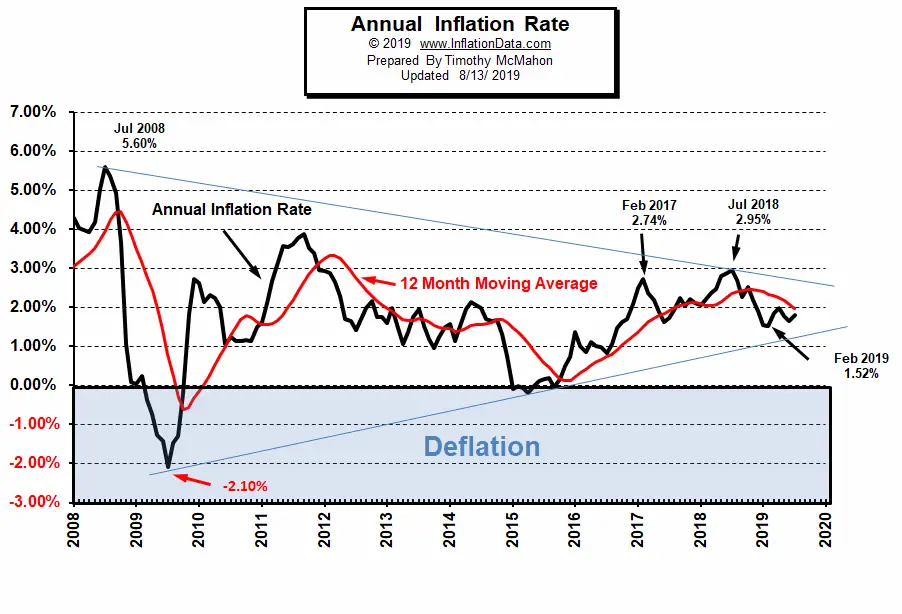
Inflation is a critical economic indicator that affects the purchasing power of consumers, the profitability of businesses, and the overall stability of economies worldwide. The latest inflation trends have become a major topic of discussion among economists, policymakers, and the general public alike. As prices rise, understanding inflation becomes more important than ever to navigate the financial landscape effectively.
Inflation is not just a number on a chart; it represents real-world consequences for households, businesses, and governments. Rising inflation can erode savings, increase borrowing costs, and lead to economic instability. In this article, we will delve into the latest inflation figures, their causes, and the measures being taken to address them.
This guide aims to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the latest inflation trends, its implications, and strategies to mitigate its effects. Whether you're an individual, business owner, or policy enthusiast, this article will equip you with valuable insights to make informed decisions.
Read also:Do Shock Sites Still Exist Exploring The World Of Online Shock Content
Table of Contents
- What is Inflation?
- Latest Inflation Trends
- Causes of Inflation
- Effects of Inflation
- Measuring Inflation
- Central Bank Policies to Combat Inflation
- Global Inflation Outlook
- Strategies for Individuals to Combat Inflation
- Impact of Inflation on Businesses
- Conclusion
What is Inflation?
Inflation refers to the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services over a period of time. It is measured as an annual percentage increase. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services, resulting in a decrease in purchasing power.
There are two main types of inflation: demand-pull inflation and cost-push inflation. Demand-pull inflation occurs when the demand for goods and services exceeds supply, driving prices higher. Cost-push inflation, on the other hand, happens when the cost of production increases, such as wages and raw materials, leading to higher prices.
Key Characteristics of Inflation
- Inflation erodes purchasing power.
- It affects different sectors of the economy in varying ways.
- Inflation can lead to economic instability if not managed properly.
Latest Inflation Trends
The latest inflation trends indicate a significant rise in prices globally. According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), inflation rates have surged in many countries due to supply chain disruptions, rising energy costs, and post-pandemic economic recovery efforts. For instance, the United States experienced an inflation rate of 8.5% in 2022, the highest in four decades.
Regional Variations in Inflation
- Developed economies like the U.S. and Europe have seen inflation rates above 7%.
- Emerging markets are experiencing even higher inflation rates, with some exceeding 15%.
- Energy-importing nations are particularly vulnerable to rising energy prices.
Causes of Inflation
Several factors contribute to inflation, including monetary policy, fiscal policy, and external shocks. Central banks play a crucial role in managing inflation through interest rate adjustments and quantitative easing. However, external factors such as global supply chain disruptions and geopolitical tensions can also drive inflation.
Key Drivers of Inflation
- Monetary expansion: Excessive money supply growth can lead to inflation.
- Supply chain disruptions: Shortages of key materials and labor can push prices higher.
- Geopolitical tensions: Conflicts and sanctions can impact global trade and energy prices.
Effects of Inflation
Inflation has wide-ranging effects on individuals, businesses, and governments. For consumers, inflation reduces the value of savings and increases the cost of living. Businesses may face higher production costs and reduced profit margins. Governments may need to adjust fiscal and monetary policies to stabilize the economy.
Impact on Different Sectors
- Households: Higher living costs reduce disposable income.
- Businesses: Increased input costs can lead to reduced competitiveness.
- Governments: Inflation can impact public spending and debt management.
Measuring Inflation
Inflation is typically measured using the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and the Producer Price Index (PPI). The CPI tracks changes in the prices of goods and services consumed by households, while the PPI measures changes in the prices received by producers. These indices provide valuable insights into inflation trends and help policymakers make informed decisions.
Read also:Exploring The World Of Erome Melayu A Comprehensive Guide
Key Indicators of Inflation
- Consumer Price Index (CPI)
- Producer Price Index (PPI)
- GDP Deflator
Central Bank Policies to Combat Inflation
Central banks around the world are implementing various policies to combat inflation. These include raising interest rates, reducing quantitative easing, and tightening monetary policy. For example, the Federal Reserve in the U.S. has increased interest rates multiple times in 2022 to curb rising inflation. Similarly, the European Central Bank (ECB) has taken similar measures to stabilize the eurozone economy.
Monetary Policy Tools
- Interest rate adjustments
- Quantitative tightening
- Forward guidance
Global Inflation Outlook
The global inflation outlook remains uncertain, with several factors influencing future trends. While central banks are taking steps to control inflation, external factors such as geopolitical tensions and climate change could continue to impact prices. The IMF predicts that inflation will remain elevated in the short term but may stabilize in the medium term if appropriate measures are taken.
Key Predictions
- Inflation rates may stabilize by 2024.
- Emerging markets may face prolonged inflationary pressures.
- Central banks will continue to prioritize inflation control.
Strategies for Individuals to Combat Inflation
Individuals can take several steps to mitigate the effects of inflation on their finances. These include diversifying investments, increasing income streams, and reducing unnecessary expenses. Building an emergency fund and investing in assets that appreciate in value, such as real estate or stocks, can also help protect against inflation.
Practical Tips
- Diversify your investment portfolio.
- Invest in inflation-protected securities.
- Create a budget and stick to it.
Impact of Inflation on Businesses
Businesses face unique challenges during periods of high inflation. Rising input costs, reduced consumer spending, and increased borrowing costs can all impact profitability. To remain competitive, businesses must adapt by improving operational efficiency, adjusting pricing strategies, and exploring new markets.
Adaptation Strategies
- Streamline operations to reduce costs.
- Adjust pricing to reflect higher costs.
- Explore alternative markets for growth opportunities.
Conclusion
The latest inflation trends highlight the importance of understanding and addressing inflation's effects on the global economy. By monitoring key indicators, implementing effective policies, and adopting proactive strategies, individuals and businesses can better navigate the challenges posed by rising prices. Stay informed, adapt to changing conditions, and take action to protect your financial well-being.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below. Additionally, explore other articles on our site for more insights into economic trends and financial strategies. Together, we can build a more informed and resilient community in the face of inflationary pressures.