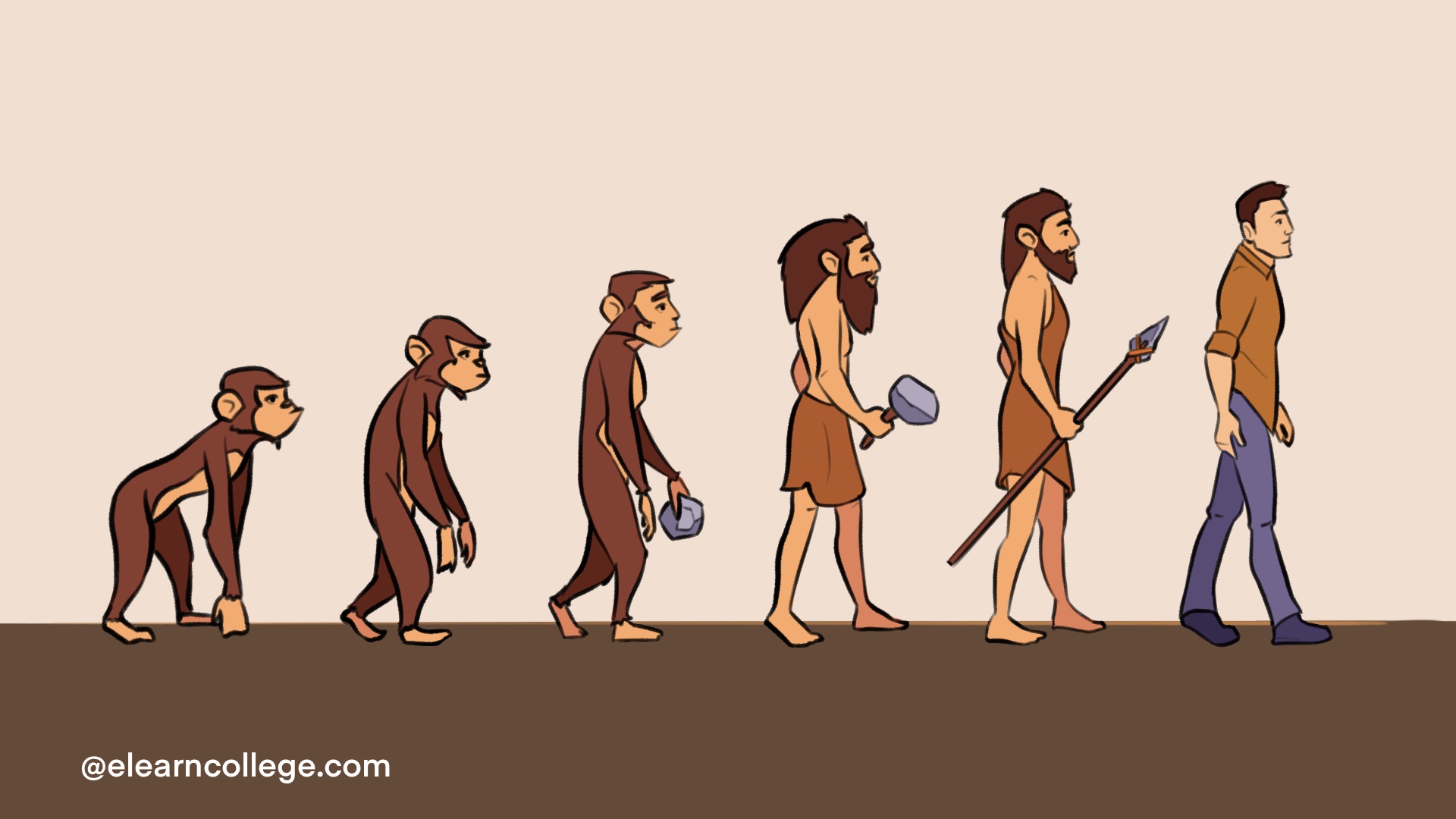
From Monkey To Human: Unraveling The Evolutionary Journey
The journey from monkey to human has intrigued scientists and laypeople alike for generations. This evolutionary path is not merely a tale of physical transformation; it reflects the complex interplay of genetics, environment, and behavior that has shaped our species. By understanding where we come from, we can better grasp the intricate web of life that surrounds us today. Despite the common misconception that humans evolved directly from modern monkeys, the truth is far more nuanced. Our evolutionary story is a tapestry woven with numerous threads, each representing different primate species that share a common ancestor with us. This article aims to explore the fascinating journey of evolution, shedding light on the pivotal milestones that distinguish humans from their primate relatives.
As we delve deeper into the monkey to human evolution, we will uncover the various stages and adaptations that have led to the emergence of Homo sapiens. From the early primates that roamed the Earth millions of years ago to the technologically advanced society we live in today, the evolutionary timeline is rich with discovery. Understanding this journey is not only crucial for comprehending our own existence but also for appreciating the diversity of life forms that inhabit our planet.
Join us as we embark on this enlightening exploration of monkey to human evolution, where we will address key questions, examine significant findings, and celebrate the remarkable story of our own species. Prepare to be amazed by the connections we share with our primate cousins and the evolutionary adaptations that have made us uniquely human.
What Are the Key Stages in Monkey to Human Evolution?
The evolutionary journey from monkeys to humans can be divided into several crucial stages, each marked by significant biological and behavioral changes. Below are some key milestones:
- Early Primates (65 million years ago): The era when the first primates appeared, resembling small, tree-dwelling mammals.
- Prosimians (55 million years ago): The development of prosimians, such as lemurs and tarsiers, who adapted to various environments.
- New World and Old World Monkeys (40 million years ago): The split between these two groups led to diverse adaptations and behaviors.
- Hominids (7 million years ago): The rise of the first hominids, marking the beginning of the human lineage.
- Australopithecus (4 million years ago): Early bipedal hominins that walked upright and exhibited both ape-like and human-like traits.
- Homo habilis (2.4 million years ago): The emergence of the first tool users, showcasing enhanced cognitive abilities.
- Homo erectus (1.9 million years ago): The first hominin to leave Africa and spread across the globe.
- Homo sapiens (200,000 years ago): The arrival of anatomically modern humans, characterized by advanced social structures and complex language.
How Did Environmental Factors Influence Evolution?
Environmental factors have played a pivotal role in shaping the evolutionary journey from monkey to human. Some key influences include:
- Climate Change: Fluctuations in climate led to changes in habitats, prompting adaptations in diet and behavior.
- Food Sources: The availability of fruits, nuts, and other food types influenced the development of teeth and digestive systems.
- Predation: The need to evade predators encouraged social behaviors and the development of communication.
- Migration: The movement of early hominins into new territories necessitated adaptations to diverse environments.
What Role Did Social Structures Play in Human Evolution?
Social structures have been crucial in the evolution of humans. Early hominins likely lived in small groups, which allowed for cooperation in hunting and gathering as well as shared child-rearing. Some aspects of social evolution include:
- Cooperation: Working together increased survival rates, particularly in harsh environments.
- Communication: The development of language facilitated complex social interactions and the sharing of knowledge.
- Culture: The transmission of cultural practices, such as tool-making and social norms, became essential for community cohesion.
How Did Bipedalism Change Our Evolutionary Path?
Bipedalism, the ability to walk on two legs, is one of the defining characteristics of humans. This significant adaptation provided numerous advantages:
- Energy Efficiency: Walking on two legs is more energy-efficient for long distances compared to quadrupedal locomotion.
- Heightened Awareness: Bipedalism allowed early hominins to see over tall grass, enhancing their ability to spot predators and prey.
- Freeing the Hands: Walking upright freed the hands for tool use, which contributed to the development of technology.
What Genetic Evidence Supports Monkey to Human Evolution?
Genetic studies have provided compelling evidence to support the theory of evolution from monkeys to humans. Key findings include:
- DNA Similarity: Humans share approximately 98.8% of their DNA with chimpanzees, indicating a close evolutionary relationship.
- Genetic Mutations: Certain genetic mutations that occurred along the human lineage are linked to unique traits, such as language and cognitive abilities.
- Fossil Record: Fossils provide physical evidence of transitional forms, showcasing the gradual changes in anatomy.
How Do Archaeological Discoveries Shed Light on Our Evolution?
The discovery of ancient tools, fossils, and artifacts has been instrumental in piecing together the story of monkey to human evolution. Key archaeological findings include:
- Stone Tools: The oldest known stone tools, dating back 3.3 million years, indicate early hominins’ ability to create and use tools.
- Fossils: Fossils of species like Australopithecus and Homo habilis provide insights into physical and behavioral evolution.
- Cave Art: Discoveries of ancient cave paintings reveal the cognitive and cultural advancements of early humans.
What Is the Future of Human Evolution?
As we continue to evolve, the future of human evolution raises intriguing questions. Factors that could influence our ongoing evolution include:
- Technological Advances: The integration of technology into daily life may lead to new forms of adaptation.
- Globalization: Increased interbreeding among diverse populations could affect genetic variation.
- Environmental Changes: Climate change and habitat destruction may drive new evolutionary pressures.
In conclusion, the journey from monkey to human is a remarkable narrative of adaptation and change. By understanding the stages of our evolution, the influences of the environment, and the role of genetics, we can appreciate the complex web of life that has shaped not only who we are today but also who we may become in the future. The exploration of our evolutionary past is not just an academic pursuit; it is a vital part of understanding our place in the world and our connection to all living beings.
You Also Like
Exploring The Life And Career Of Bob Blanchett: A Multifaceted TalentUnveiling The Mystery: Raven-Symoné's Daughter Age
Celebrating Love: The Enchanting Rebecca Pritchard Wedding
What Does Aaron Donald's Brother Do? Unveiling The Life Of An NFL Sibling
Exploring Barron Trump And His Connection To The LGBT Community